Page 8 - IJEEE-2023-Vol19-ISSUE-1
P. 8
4| Almousawi & Aldair
surplus load. Consequently, when generation exceeds load,
"%& rises over its reference value, and HESS charges to The HESS charge/discharge mechanism is regulated by
receive the excess power. The discharge/charge HESS the #'( output and the specific #)*+, . The buck charging
current is controlled by the four converters using a double converters redirect the excess #'( to charge the HESS, while
loop control scheme to avoid overlap appearing in [30]. the boost discharging converters supply the HESS's
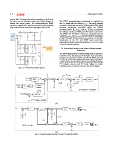
necessary power. "-& , "./--, and "'( in Fig. (2) represent
Fig. 2: PV-BESS-SC Hybrid System the voltages of a SC, a BESS, and a PV panel, respectively.
SC, BESS, and PV panel currents are represented by the
variables %-&, %., and %'(. &'( indicates the filter inductance
of the PV panel's boost converter. &-& and &. are the filter
inductances of the SC and BESS boost converters,
respectively, while R is the load resistance. S", S#, S$, S0, and
S1 are the control switches.
IV. PROPOSED CONTROL AND ENERGY MANAGEMENT
STRATEGY
The block diagram of the control strategy used in this paper
is shown in Fig. (3). Because of its higher noise protection,
average current mode control is used for the BESS, SC, and
PV panels, and it offers additional robust voltage regulation.
A first-order Low Pass Filter (LPF) is used for BESS current,
PV inductor current, and DC load voltage to reduce
switching noise, measurement noise, and current ripple.
(a)
(b)
Fig. 3: Control System Structure for (a) PV Panel (b)-HESS.